Havoc in heaven
Mohan Mainali / July 4, 2016
Revisiting what used to be Langtang village, after 17 years
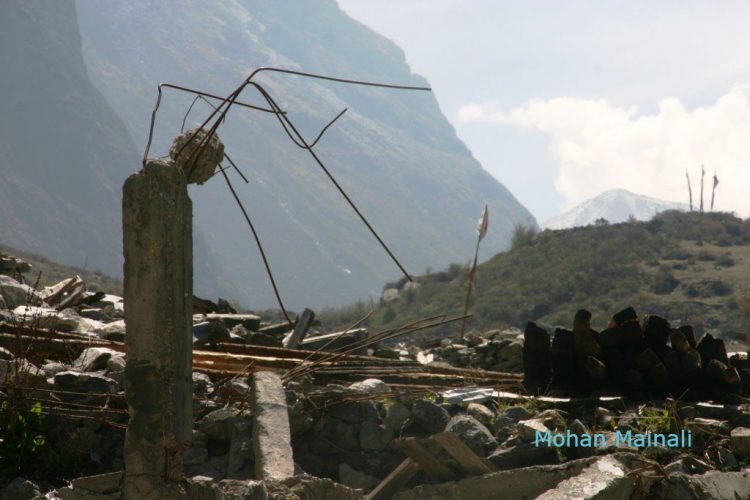

Concrete pillar with iron arms is mute testimony to the devastation wreaked by the Langtang avalanche.
Arriving in Langtang after 17 years, video editor Rabindra Pandey looked east from Gumba Danda. He hoped to see some of the quaint stone houses he had filmed in 1999, and scanned around for the Nepal Army checkpost guarding the Langtang National Park. There used to be a micro-hydropower plant by the river. There used to be a river.
But to his shock and dismay, everything was gone. Only a vast terrace of white rock and sand, and fluttering prayer flags, were visible where the homes used to be. “It was worse than a war zone, at least you see ruins of buildings after a war,” Pandey said, walking across a field of huge boulders.
Previously 130 houses stood here but except for one house under the cliff, none of them remains. On 25 April, Langtang was first shaken by an earthquake, and a minute later it was obliterated by the shockwave preceding a gigantic avalanche of ice and rock that tumbled down the mountain. Scientists estimate that 7 million cubic metres of rubble came down on the village, enough to cover 10 football fields with rocks 100 m thick. The blast wave was so strong that most bodies were found on the other side of the valley, where an entire pine forest was flattened.
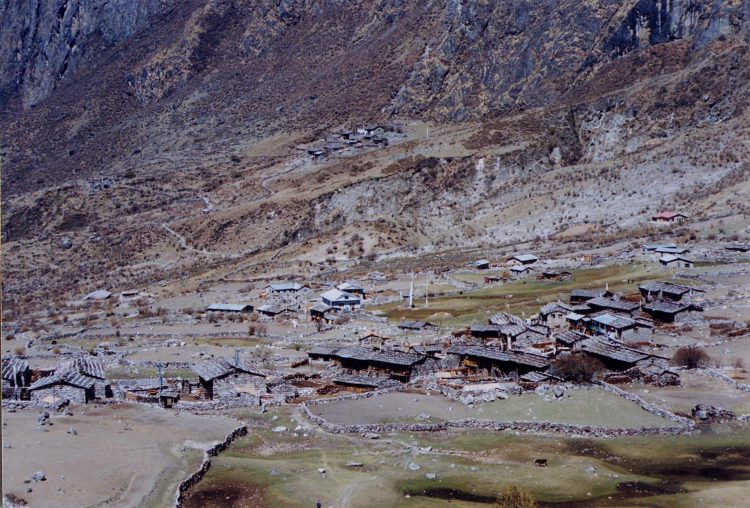

YESTERDAY AND TODAY: Langtang village from a film by Rabindra Pandey 17 years ago, and a view of the same spot after a massive avalanche triggered by last year’s earthquake swept the village away.
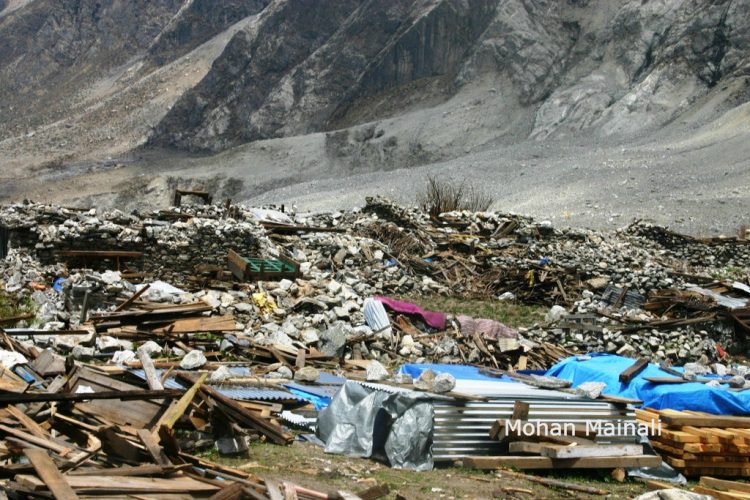

Beyond the debris field, we were glad to see that some houses were intact. Villagers gathered around Pandey’s laptop to watch video clips he had shot 17 years ago, pointing at relatives they recognised but who had perished in the avalanche.
Estimates vary, but locals say up to 350 persons died on 25 April, among whom were 93 men and women between the ages of 25 and 40. Said village elder Subba Tamang: “We lost most of our able-bodied neighbours and relatives, we lost people who could carry out rituals, prayers, singing and dancing, people who could build homes and help tourists.”
Pasang Dondup had dashed out of his house when it started shaking at 11:56 am on that fateful day. He heard a terrible roar from somewhere above the clouds, and ran into his brother’s house to hide but remembered his daughter and rushed back to his own dwelling. By that time the avalanche was already pressing him to the wall of his brother’s house. The sky went dark. He screamed, and looked around to see that his village was gone, his wife had disappeared. He never found her body.
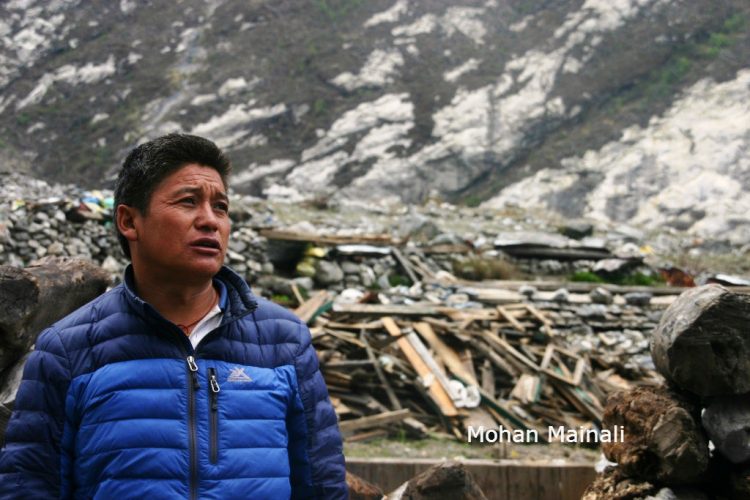

Subba Tamang is critical of the delay in help for rebuilding and the tax on construction timber.
The next day he walked down to Trishuli, and on to the Yellow Gumba in Swayambu where he spent four months with other Langtang villagers. When we saw him recently, he had just returned to Langtang. All the savings he had poured into building his house was gone, along with all his possessions. His farm and pasture are gone. Despite three operations on his injured hand, the wounds have not healed.
“It was unimaginable, nature left me like this,” Dondup says. His predicament is the same one faced by hundreds of others in Chamki, Gumba Danda and Langtang, which the avalanche also wiped out.
The earthquake could not have happened at a worse time. That winter, an unprecedented blizzard had deposited a record amount of snow on the slopes of Langtang.
Tamang is trying to get the phone network functioning again, and rebuilding both homes and lodges since tourism is the mainstay of the Langtang economy. Although the Valley used to receive 14,000 trekkers a year, this spring only saw 2,000. The National Park generally earned Rs 40.5 million a year in fees, but the earthquake slashed that figure substantially.
Even the Army and government offices are still in ruins, so it is not surprising that damaged homes have not been rebuilt. Part of the problem is that the National Park has not waived the charges of Rs 100 per cubic feet and 13 per cent VAT on timber from the forest.
Tamang cannot understand why the government is so strict: “Is this how it is in other countries that have suffered disasters? I don’t think too many people are coming back to Langtang. The younger people, at least, aren’t returning.”
First published in Nepali Times 1-7 July 2016
This material is copyrighted but may be used for any purpose by giving due credit to southasiacheck.org.
Comments
Latest Stories
- In Public Interest Covid-19 cases are low, but that’s not an excuse to avoid vaccination
- In Public Interest What is BF.7, the sub-variant that has the world by its grip?
- In Public Interest Threat of a new Covid-19 wave looms large amid vaccine shortage in Nepal
- In Public Interest As cases decline, Covid-19 test centres in Kathmandu are desolate lot
- In Public Interest Dengue test fee disparity has patients wondering if they’re being cheated
- In Public Interest As dengue rages on, confusion galore about what it is and what its symptoms are. Here’s what you need to know
In Public Interest
 Covid-19 cases are low, but that’s not an excuse to avoid vaccination
The Pfizer-BioNTech bivalent vaccines authorised by the Nepal Government provide better protection a...
Read More
Covid-19 cases are low, but that’s not an excuse to avoid vaccination
The Pfizer-BioNTech bivalent vaccines authorised by the Nepal Government provide better protection a...
Read More
- What is BF.7, the sub-variant that has the world by its grip?
- Threat of a new Covid-19 wave looms large amid vaccine shortage in Nepal
- As cases decline, Covid-19 test centres in Kathmandu are desolate lot
- Dengue test fee disparity has patients wondering if they’re being cheated
- As dengue rages on, confusion galore about what it is and what its symptoms are. Here’s what you need to know